The 2021 HealthStream Clinical Industry Report

Introduction
HealthStream is pleased to bring you the 2021 Clinical Industry Report. This report examines the top data findings and trends across our ecosystem. The HealthStream 2021 Clinical Industry Report is designed to provide insight into key findings related to clinical competency development for clinical and education leaders.
We reviewed data from a multitude of sources, from national surveys to insurance claims data to completion data from HealthStream’s platform. After a thorough review, we identified four top areas of concern across our ecosystem we think merit further review and consideration:
Each area of concern is presented in detail within the report and includes findings specific to the most important discoveries within our data sources. These findings demonstrate what facilities and clinical professionals across the country have been experiencing before, during and after a turbulent 2020. You can find out more about our sources in the appendix.
We hope this information is helpful and informs decision-making in your own organization. Please don’t hesitate to share your comments with us, as well as insights you have on these findings and others that you may be experiencing in your area of the country.
We wish you and your team the very best for 2021 and beyond.
Finding One
AI technology identifies gaps between actual versus self-reported confidence in clinical problem recognition.
Key Takeaways
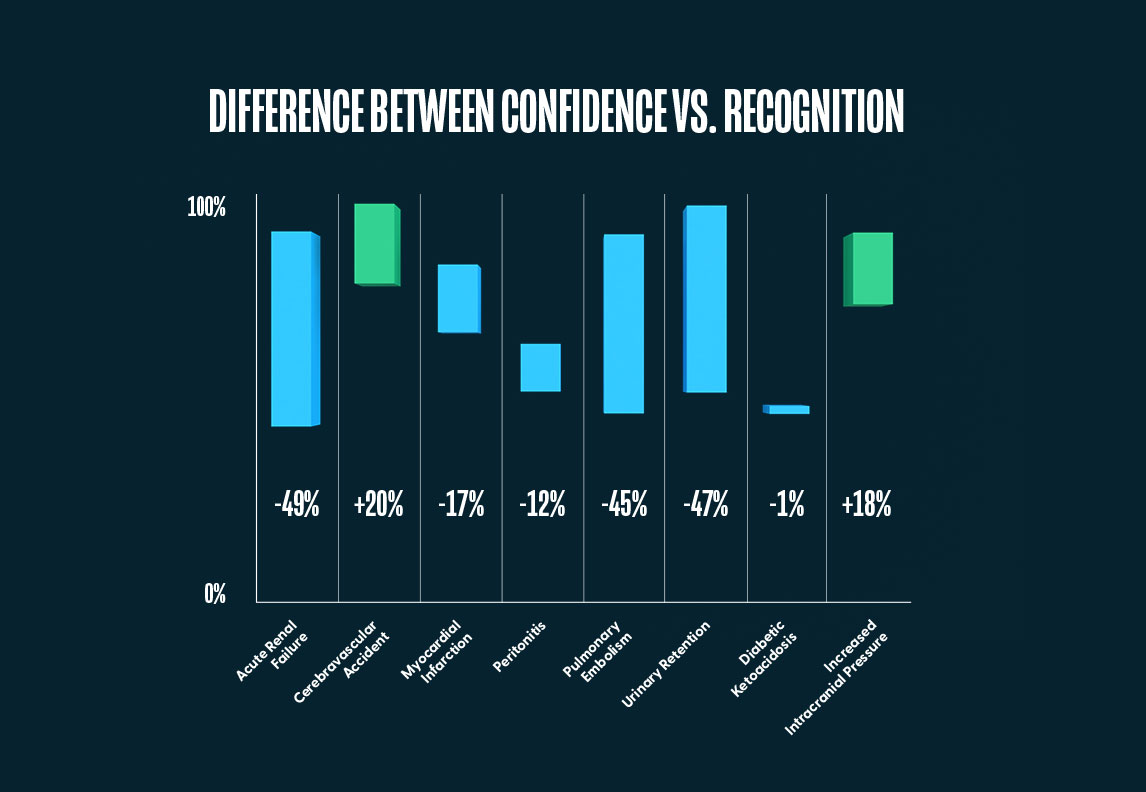
1. Acute Care Nurses are overconfident in their ability to recognize and manage Pulmonary Embolism, Acute Renal Failure, Myocardial Infarction, and Urinary Retention.
2. At the same time, they are under-confident in their ability to recognize and manage Diabetic Ketoacidosis and Cerebrovascular Accident.
HealthStream’s 2021 Nurse Confidence Survey was conducted to better understand how registered nurses rated their own confidence related to specialty-specific clinical problems. Participants were asked to rate their confidence on a 5-point scale (Strongly Agree to Strongly Disagree) in recognizing and managing a variety of different clinical problems.
Based on the specialty area chosen on the national nurse confidence survey, participants were asked a series of questions about
their confidence in recognizing and managing different clinical problems. The questions were phrased as follows:
There were 3,446 nurse participants who identified Medical-Surgical or Telemetry as their primary specialty and/or area where
they worked the most hours in 2020. This group was asked specifically to rate confidence with the following emerging problems:
These responses were then compared to data derived from 592 registered nurses who completed assessments during 2020 for these emerging clinical problems with the Jane Acute Care AI assessment via HealthStream’s learning platform.
The Jane program is unique in that it was trained by leveraging artificial intelligence powered by IBM Watston and the Performance Based Development System (PBDS) database to identify problems, observations, actions and rationale based on the model answers established by the PBDS. In studies evaluating the effectiveness of Jane to assess a nurse’s competency levels, it was found that Jane and human raters agreed 82.7% of the time.
This study assumed that accurate identification of the problem was a prerequisite for effective management – in other words, a nurse who can recognize the problem and seek help meets the minimum definition of effectively “recognizing and managing the problem.”
The results presented here compare the percentage of nurses that accurately identified the problem to the percentage of nurses who indicated Strongly Agree or Moderately Agree for each of the emerging problem confidence statements. With each result, we provide a 95% confidence interval to discern if there is a significant difference between the two means for each clinical problem.
For both Cerebrovascular Accident and Diabetic Ketoacidosis, the percentage of nurses who agreed they could recognize and manage the problem was lower than the percentage of nurses that were actually able to. While this may be due to discrepancies in the understanding of management versus problem identification, it should be noted that with both emerging problems, nurses performing their assessments via Jane did list the action of “notifying the provider” over 99% of the time, indicating they did in fact recognize a problem and would therefore seek assistance.
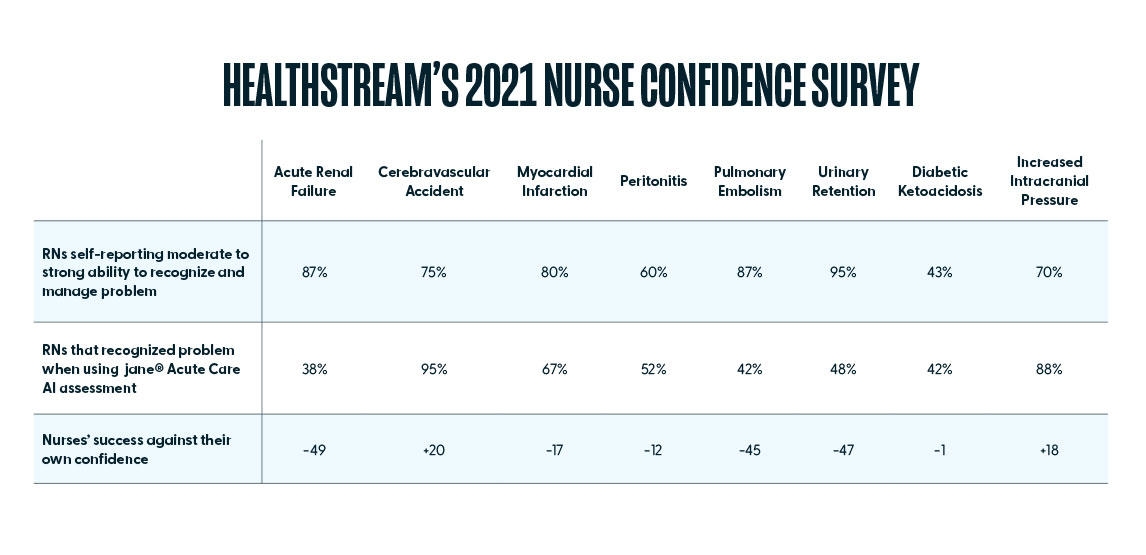
While several of the problems revealed overconfidence discrepancies, the largest was with Acute Renal Failure. While 87% (CI [86.2%, 88.4%]) of acute care nurses agreed that they could recognize and manage this problem, only 38% (CI [34.4%, 42.2%]) actually did on the Jane AI Assessment. Interestingly, there was no real discrepancy between self-reported confidence and actual results with Increased Intracranial Pressure. While 43% (CI [41.7%, 45.0%]) of acute care nurses agreed that they could recognize and manage this problem, and 42% (CI [38.5%, 46.4%]) actually did on the Jane AI Assessment.
Finding Two
Competency development systems can reduce the time and money spent developing staff
Key Takeaways
1. The University of Louisville Hospital reduced the time spent managing assessment and development of nurses by 50% using HealthStream’s Jane.
2. San Juan Regional Medical Center saved an average of $280 per nurse using HealthStream’s Jane.
San Juan Regional Medical Center (SJRMC) is a 194-bed, nonprofit, community owned hospital. Though they had been utilizing the Performance Based Development System (PBDS) to assess nurse competency for 19 years, the growing organization needed to adapt to changing clinical needs. They needed a program that offered a more detailed description of nurse progress, indicators for targeting strengths and weaknesses, feedback on and prioritization of problems, and the precision of a quantifiable score as opposed to a rating.
In late 2019, they implemented Jane and began using it with new graduate nurses, transitioning staff, and traveling nurses. Leaders noted that with transitioning nurses, Jane provided assessment of competency gaps, recommendations for personalized competency plans at scale, and evidence-based learning options. After implementation, they experienced a reduction in CLABSI and CAUTI, two common healthcare-acquired infections (HAIs), due to their improved orientation program that includes Jane. Significant time and cost savings were other valued impacts. SJRMC estimated that educators saved an average eight hours per nurse assessment by reducing the time spent preparing, proctoring, reviewing results, writing plans, and meeting with students or managers. At an average rate of $35-per-hour for a registered nurse, that is an average savings of $280 per nurse.
The University of Louisville (UofL) Hospital is an academic teaching and research hospital that is part of UofL Health, a fully integrated regional academic health system with five hospitals, four medical centers, and multiple other care facilities. They had been using a manual nurse assessment method that was effective though time-consuming to implement and operate. Education coordinators knew this solution would not scale well for consistent use across all hospitals in the system, which was the end goal.
In early 2020, they decided to add HealthStream’s Jane, a dynamic system that identifies gaps and recommends personalized nurse competency plans across the knowledge and clinical judgment domains. They chose Jane specifically because they wanted to transition from time-consuming manual processes to a more standardized approach. After the roll out in January 2020, UofL Hospital coordinators quickly found themselves pivoting to use Jane to rapidly assess new nurses and efficiently transition existing nurses to additional areas of need, in response to changing care demands during the COVID-19 pandemic.
During the first 90 days of using Jane, they experienced a 50% reduction in time spent managing assessments. The increased speed in delivery of testing, grading, and analysis made it possible for them to complete more than 270 assessments during that time period. Jane also provided the unexpected benefit of allowing the hospital to react quickly during the COVID crisis with minimal disruption.
Finding Three
Almost half of the 25M courses completed on the HealthStream platform in 2020 were self-enrolled
Key Takeaways
1. Of all course completions in 2020, 48.4% were self-enrolled. The top self-enrolled course for 2020 was NIH Stroke Scale Training and Certification.
2. Surveys indicated 65% of new graduate nurses with less than one year of experience would be interested in a digital mentor, like Jane, that makes course recommendations.
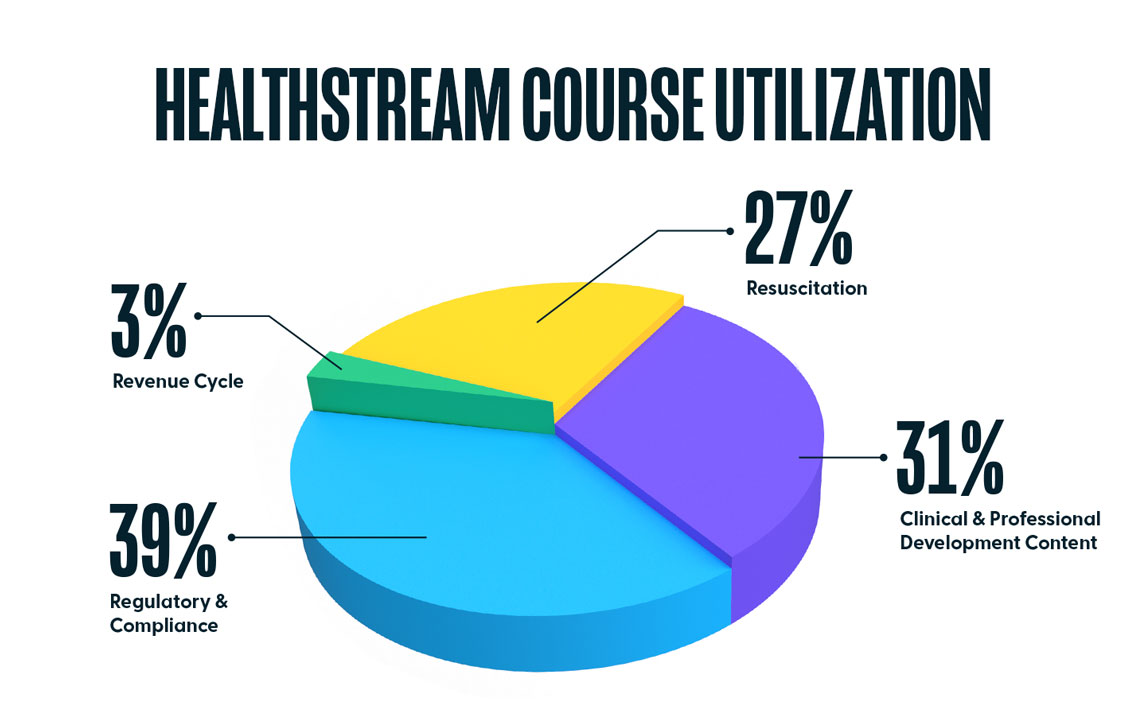
In 2020, over 25.6 million courses were completed on the HealthStream platform, suggesting an increased interest in self-enrollment by clinicians. Regulatory and Compliance were most popular, making up 39% of all courses completed. Clinical and Professional Development Courses made up 31% of all completions, Resuscitation made up 27%, and Revenue Cycle courses made up the remaining 3%.
Of the 25.6 million course completions, nearly half (12.4M) were self-enrolled. The top 3 most popular self-enrolled courses in 2020 were the following:
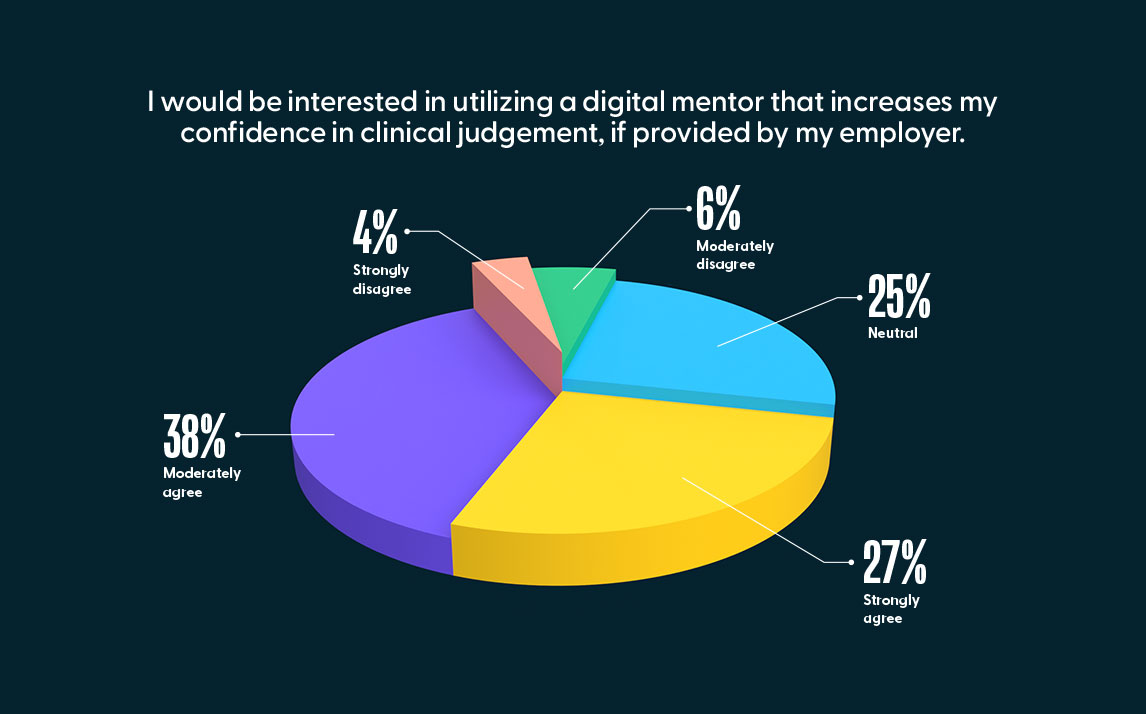
Self-enrollment continues to increase in popularity as a practical and convenient way for nurses to obtain required training as well as training in specialty areas of interest. As the Jane Competency Development system continues to evolve, we anticipate further increases in the self-enrollment percentage, particularly due to the program’s ability to recommend courses that nurses can easily view and self-enroll in based on assessment results. On the national nurse confidence survey, when we asked the 727 Registered Nurses with less than one year of experience if they would be interested in utilizing to a digital mentor that increases their confidence in clinical judgment, if provided by their employer, 65% of them either moderately agreed or strongly agreed.
Finding Four
Department-specific courseware for specialty care contributes to improved outcomes
Key Takeaways
1. HealthStream customers using the Quality Obstetrics (OB) Program had 22% less “OB risk claims identifiers” versus all hospitals in the U.S.
2. HealthStream customers using the Quality Emergency Care (EC) Program had an average of 60% fewer “EC risk claims identifiers” versus all hospitals in the U.S.
In order to assess whether department-specific courseware can contribute to improved outcomes in those specialties, HealthStream reviewed full-year historical claims data from its partner Perception Health for 2019 and 2020. Utilizing the HealthStream Quality OB and Quality EC programs as examples, the intent was to determine whether their usage resulted in a lower percentage of risk claim identifiers, based on ICD-10/CPT codes as determined by a medical coding expert. The codes were chosen because they appeared when insurance was billed for patients who did not meet outcomes of clinical presentation. The results are grouped according to customers who used either HealthStream product versus all hospitals that submitted similar claims.
Quality OB
The HealthStream Quality OB program maximizes team-based performance in obstetric care through competency-based modules related to high-risk patient safety issues. The audience for this program is nurses, mid-level providers and physicians. The included modules are:
For this program, Dr. Henry Lerner determined the codes that would be most indicative of clinical presentation in patients whose outcomes are not met. Dr. Lerner is the founder of Newton-Wellesley Obstetrics & Gynecology. A graduate of Princeton University and Harvard Medical School, he completed his residency training in Obstetrics and Gynecology at the University of California, San Francisco. He is Board Certified in Obstetrics and Gynecology and an Assistant Clinical Professor of Obstetrics and Gynecology at the Harvard Medical School.
The ICD-10/CPT codes identified by the HealthStream team and Dr. Lerner were sent to Perception Health, which determined the total number of OB risk claim identifiers for all hospitals in the United States for full year 2019 to be used as the numerator. Next, Perception Health isolated the total number of births for all hospitals in the United States for full year 2019 to be used as the denominator. Finally, this data was used to determine the overall number of OB risk events as a percentage of births for all hospitals in the United States, and for all hospitals using the HealthStream Quality OB Program.
The percentage of OB risk claim identifiers for 2,962 hospitals that had commercial insurance birth claims data for full year 2019 was 5.7% (CI [5.69%, 5.77%]). The percentage of OB risk claim identifiers for the hospitals that used the HealthStream Quality OB Program for full year 2019 was 4.4% (CI [3.17%, 5.12%]), which is 22% less OB risk claim identifiers compared to all U.S. hospitals.
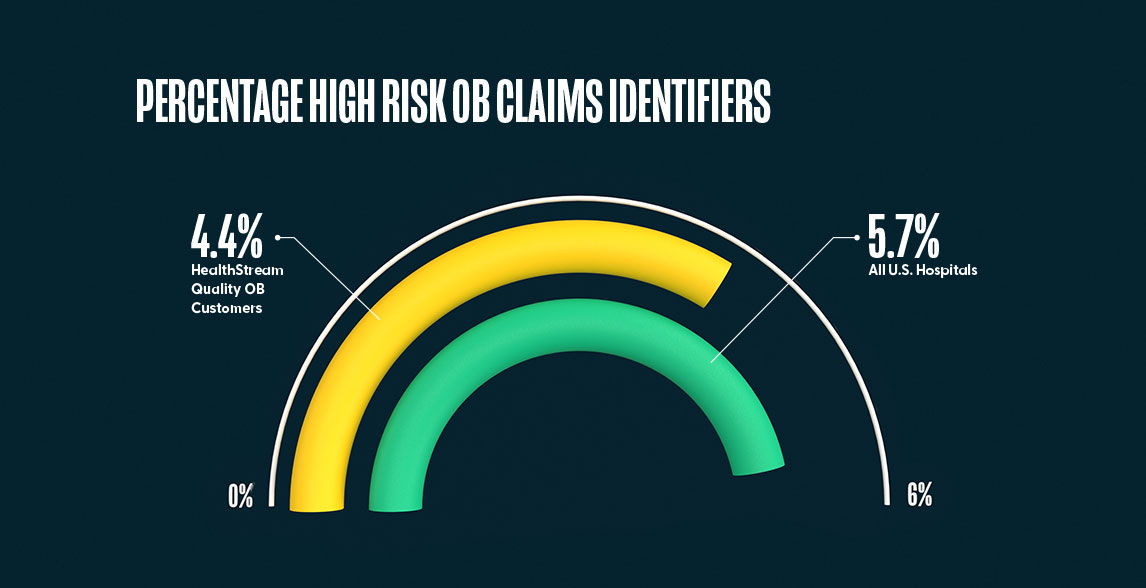
By providing the competency-based OB modules related to high-risk patient safety issues to nurses, mid-level providers and physicians, the hospitals using the Quality OB Program saw a decrease in obstetrical complications as evidenced by the lower percentage of OB risk claim identifiers.
Quality EC
The goal of the Quality EC Program is to decrease adverse patient outcomes resulting from commonly missed diagnoses in an Emergency Care setting. This program consists of 16 scenario-based modules divided into five key topic areas:
To determine the codes for the Quality EC program, HealthStream utilized the expertise of Dr. Daniel Davis. Dr. Davis completed his undergraduate training in neuroscience at UCLA, where he was a National Merit, Regents, and Alumni Scholar. He graduated Magna Cum Laude and attended the UCSD School of Medicine, where he remained for his residency training in emergency medicine. He has published over 200 original articles in peer-reviewed journals, received numerous research awards and grants, and served as Principal Investigator for the prestigious Resuscitation Outcomes Consortium. Dr. Davis’ most impactful work to date has been the development of the Advanced Resuscitation Training (ART) program, which uniquely links performance improvement data and training to reduce preventable deaths in the hospital and prehospital environments.
The average number of EC risk claim identifiers for 9,490 U.S. hospitals for full year 2019 and full year 2020 was 8.19 (CI: [7.82,8.56]) events per hospital. For the 55 hospitals that have been actively using the HealthStream Quality EC program it was 3.27 (CI: [2.11, 4.42]) events, or 60% fewer “high risk claim identifiers” for the hospitals using the Quality EC program.
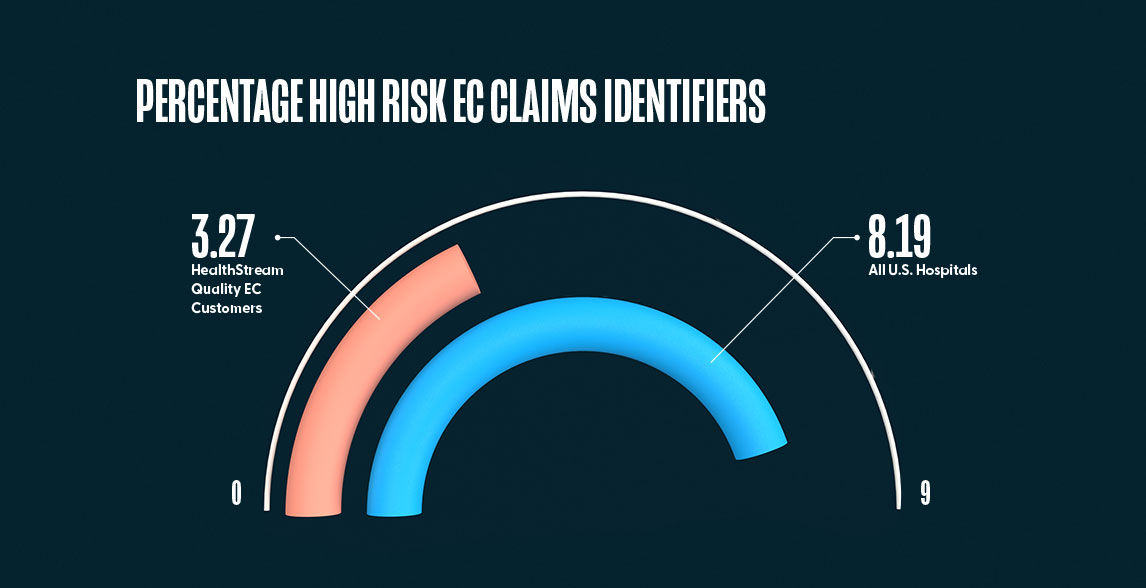
Finding Five
Cardiopulmonary events increased in 2020 due to COVID-19, but results according to month, location and population density reveal other disparities
Key Takeaways
1. Although similar in population size, the number of commercial insurance claims for cardiopulmonary resuscitation per 100,000 residents was 1000% greater in Washington D.C. (55 per 100,000) versus Alaska (5 per 100,000) in 2020.
2. 2020 saw the largest number of commercial insurance claims for cardiopulmonary resuscitation in the past 5-years.
3. On average, September had the lowest number of claims, and December had the highest over the past 5-years.
In-hospital CPR is of critical importance for surviving a cardiac or respiratory event, but there is also a steep cost associated with this life-saving measure. In this study, we evaluated 342,343 commercial insurance claims filed for Current Procedural Terminology (CPT) code 92950 from 2016 – 2020. CPT 92950 is defined as “CPR performed to restore and maintain the patient’s respiration and circulation after cessation of heartbeat and breathing.” Over this period, more than $346.7M was billed for this CPT alone.
Results indicated there was an 11.7% increase in billing events for CPT 92950 between 2019 and 2020. The cumulative number of events began to outpace 2019 starting in June 2020. As would be expected, the data also shows a positive proportional correlation between COVID-19 deaths and number of resuscitation events each month.
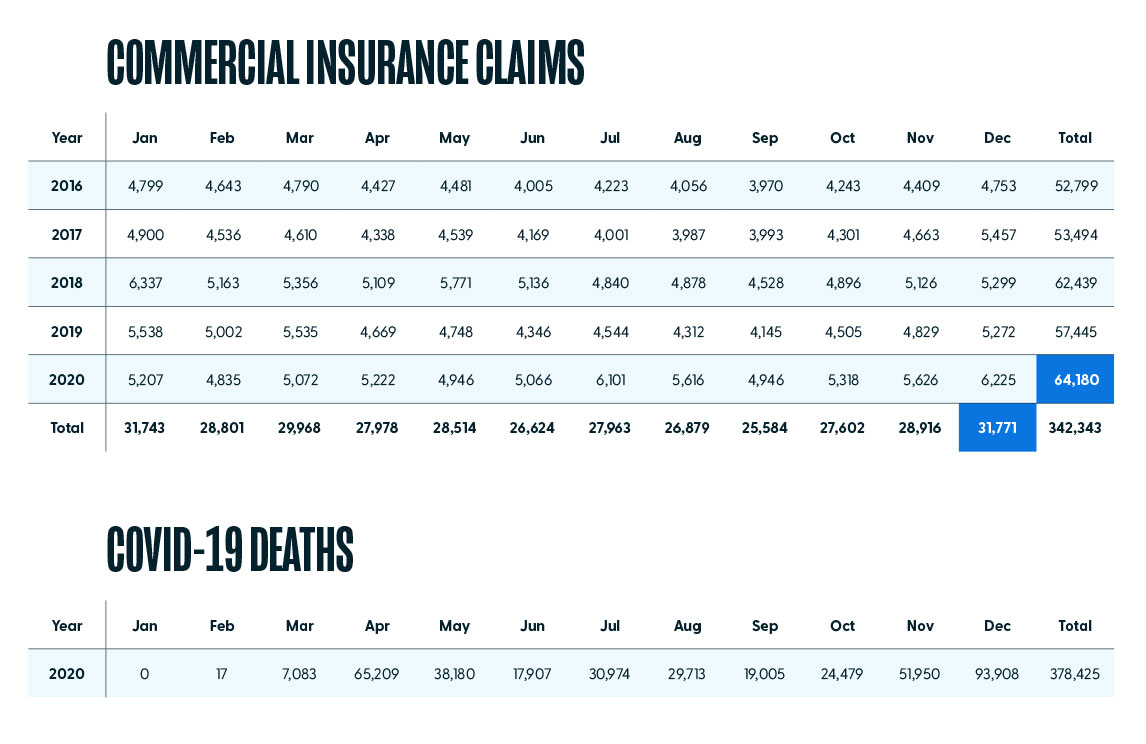
However, in reviewing the past five years, it is clear the number of cardiopulmonary events is not evenly distributed over each month. Despite the influence of the pandemic, some months outpace others, indicating a consistent, higher incidence of events at certain times of the year. Further, events are not evenly distributed over each of the states. In 2020, Texas had the largest number of events (6,324) billed to commercial insurance, while Alaska had the lowest (40).
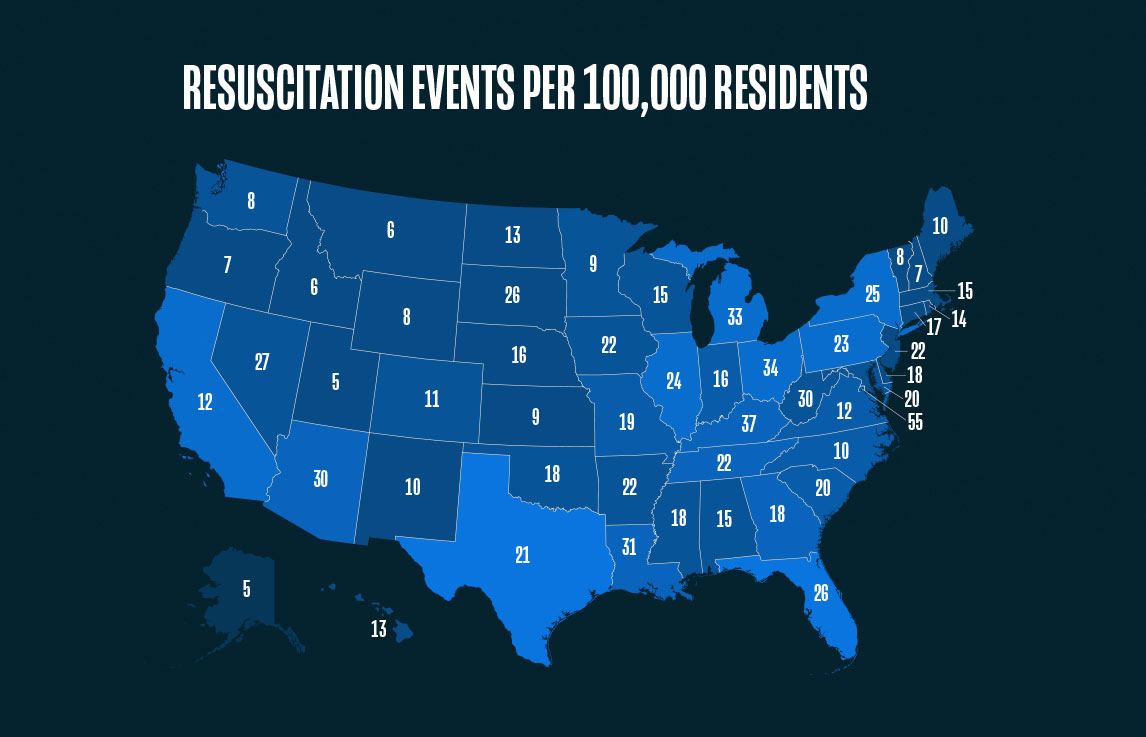
Looking at the total number of events per state is only a part of the story. The number of events per 100,000 residents shows a different trend. For instance, Washington, D.C. had the highest percentage of population resuscitation events in 2020 (55 per 100,000 residents) whereas Alaska and Utah were tied for the lowest percentage of population resuscitation events in 2020 (5 per 100,000 residents).
Finding Six
Nurses’ confidence in their ability to provide CPR is high, but further training is needed to prevent cardiac events altogether
Key Takeaways
1. A study of Dr. Daniel Davis’ Advanced Resuscitation Training (ART Program) completed at the University of California shows that early detection concepts resulted in a decrease in cardiac arrests of non-ICU patients by more than 50%.
2. AI Competency Development Systems, like Jane, help to assess and develop confidence in early detection concepts.
CPR is a fundamental part of any nurses’ training, and clinicians consistently demonstrate a strong understanding of the science behind it. For instance, the 27,576 unique users who completed the American Red Cross Basic Life Support course on the HealthStream platform in 2020 had an average final score of 91.17%.
With such high assessment scores, it is not surprising to find nurses are also confident in their ability to provide effective CPR. Of the 9,556 nurses that responded to HealthStream’s 2020 national nurse confidence survey, 88% (CI: [86.21%, 89.79%]) of nurses either moderately agreed or strongly agreed with the statement, “I am confident in my ability to provide effective CPR.”
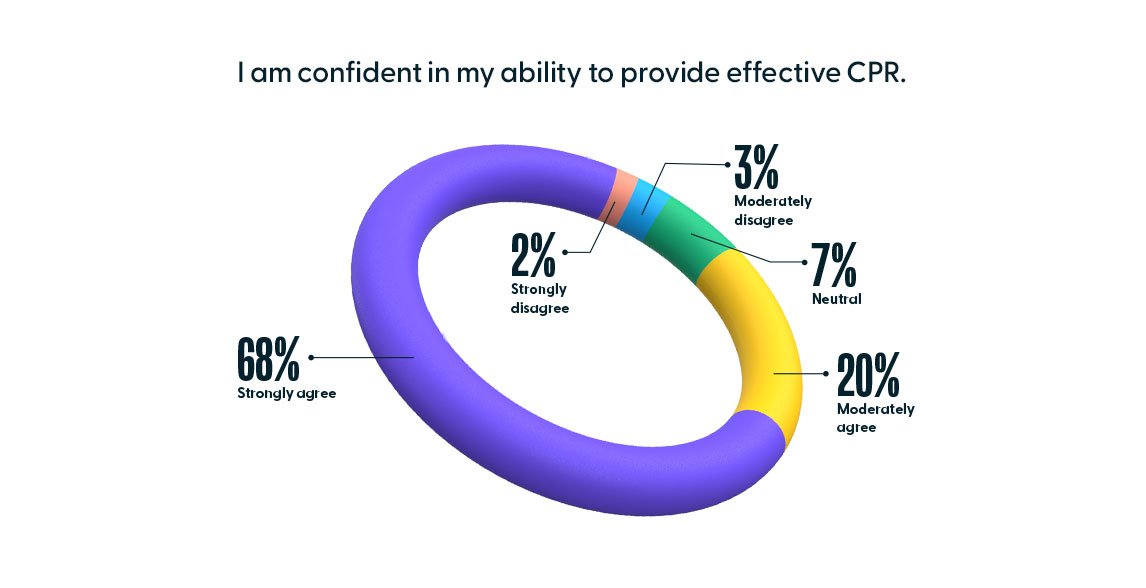
However, the levels of skill and confidence do not match up with survival rates, which indicate only 34% of patients who receive resuscitation will survive until discharge. This disparity, according to a study completed by Dr. Daniel Davis, is due to early detection rather than proper CPR technique.
According to Dr. Davis, early detection concepts resulted in a decrease in cardiac arrests in non-ICU inpatient units by more than 50%. An increase in survival-to-hospital discharge from 21% to 45% (p < 0.01) was observed following ART program implementation. Adjusted odds ratios for survival-to-discharge (OR 2.2, 95% CI 1.4–3.4) and good neurological outcomes (OR 3.0, 95% CI 1.7–5.3) reflected similar improvements. Arrest-related deaths decreased from 2.1 to 0.5 deaths per 1,000 patient discharges in non-ICU areas and from 1.5 to 1.3 deaths per 1,000 patient discharges in ICU areas. Overall hospital mortality decreased from 2.2% to 1.8%.
On the national nurse confidence survey, nurses were slightly more confident in early recognition of a deteriorating patient than they were in their confidence in providing CPR. Of the 9,556 nurses that responded to the national nurse confidence survey, 90% (CI: [88.15%, 91.85%]) of nurses either moderately agreed or strongly agreed to the statement, “I am confident in my ability to quickly recognize a deteriorating patient prior to them needing CPR.”
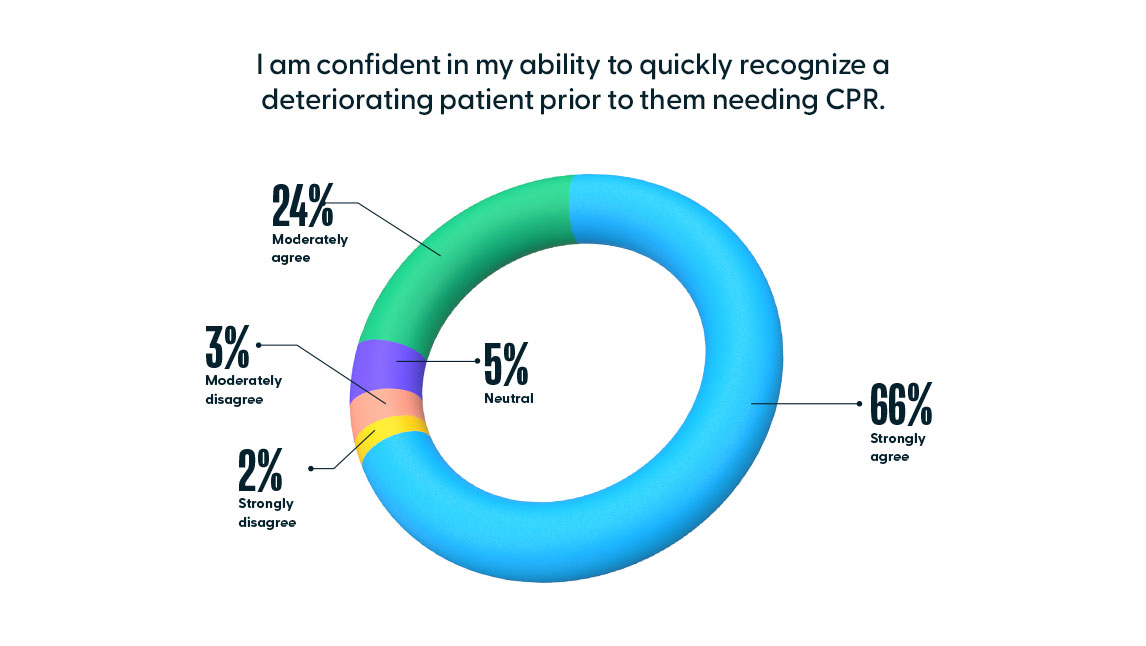
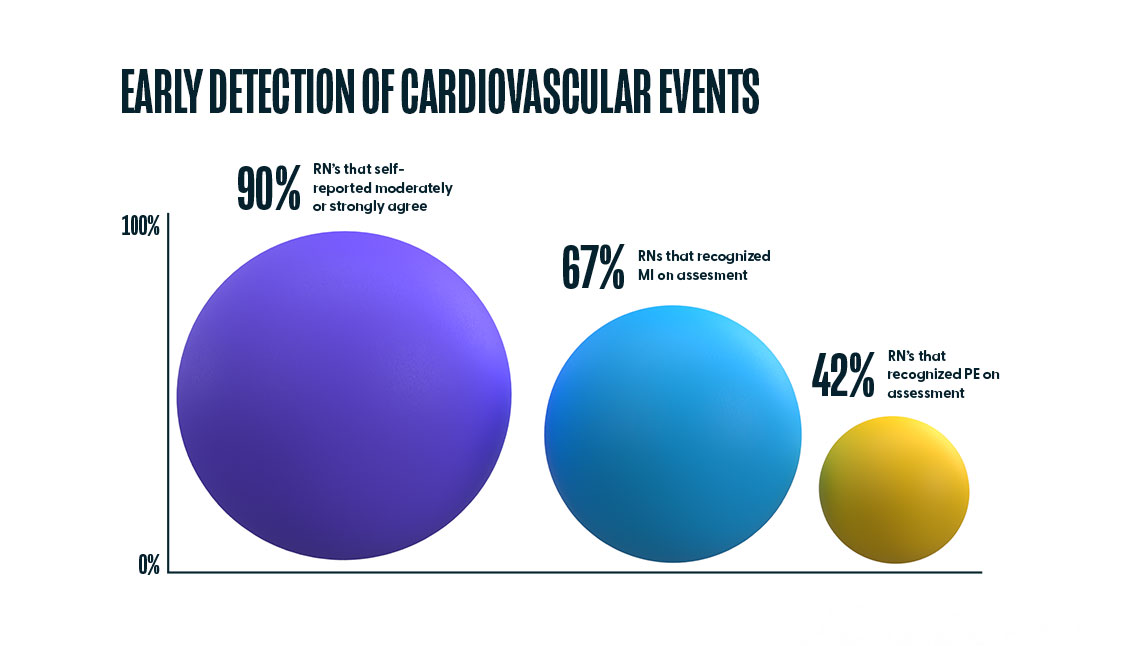
When we compare this overall confidence in “quickly recognizing a deteriorating patient” (90%) with the percentage of nurses that accurately recognized the emerging problems of Myocardial Infarction (67%) and Pulmonary Embolism (42%), two diagnoses that if not recognized and treated early, lead to a cardiopulmonary event, there is a discrepancy. Further training in this area can develop a clinician’s ability to quickly recognize and treat a deteriorating patient, thus reducing the need to perform CPR in the first place.
Finding Seven
COVID-19 Training is in high demand, with HealthStream delivering training for more than half of all registered nurses in the U.S.
Key Takeaways
1. The HealthStream platform delivered over 4.1 million COVID-19 Courses at a pace of ~9.4K courses per day to over 2 million unique users.
2. Stress and uncertainty took a toll on nurse confidence in 2020.
By the close of 2020, per the CDC, COVID-19 was listed as the underlying or contributing cause of 377,883 deaths (91.5 per 100,000 population), making it the third leading cause of death in the United States. With the rapid spread of COVID-19 and new information about the virus coming out almost daily in 2020, it was imperative to get useful information into the hands of frontline workers. To combat healthcare workers’ low confidence and concerns, HealthStream offered 182 free COVID-19 courses in 2020. In addition to these courses, HealthStream customers utilized the hStream platform to provide facility-specific COVID-19 training.
As a result, there were over 4.1 million completions of COVID-19 content, consumed at an average rate of approximately 9.4K courses per day by over 2 million unique clinicians. A total of 71.2% of all HealthStream users are Registered Nurses, which equates to 1.4 million Registered Nurses being trained. According to the BLS, there were approximately 2.4 million Registered Nurses actively working in clinical settings in 2020. The HealthStream platform was there to support the COVID-19 training for more than 58% of all actively working Registered Nurses in the U.S.
It is unlikely the demand for such programs will abate post-pandemic, given the associated levels of stress clinicians faced. To assess confidence and stress levels among nurses, HealthStream launched a 10-question survey in April 2020. The survey included questions about confidence to care for COVID-19 patients, equipment shortages, and other concerns. Of the 14,406 clinicians surveyed, of which 89% were Registered Nurses, the majority (47%) was only somewhat confident in their ability to care for COVID-19 patients, and 20% were not confident at all.
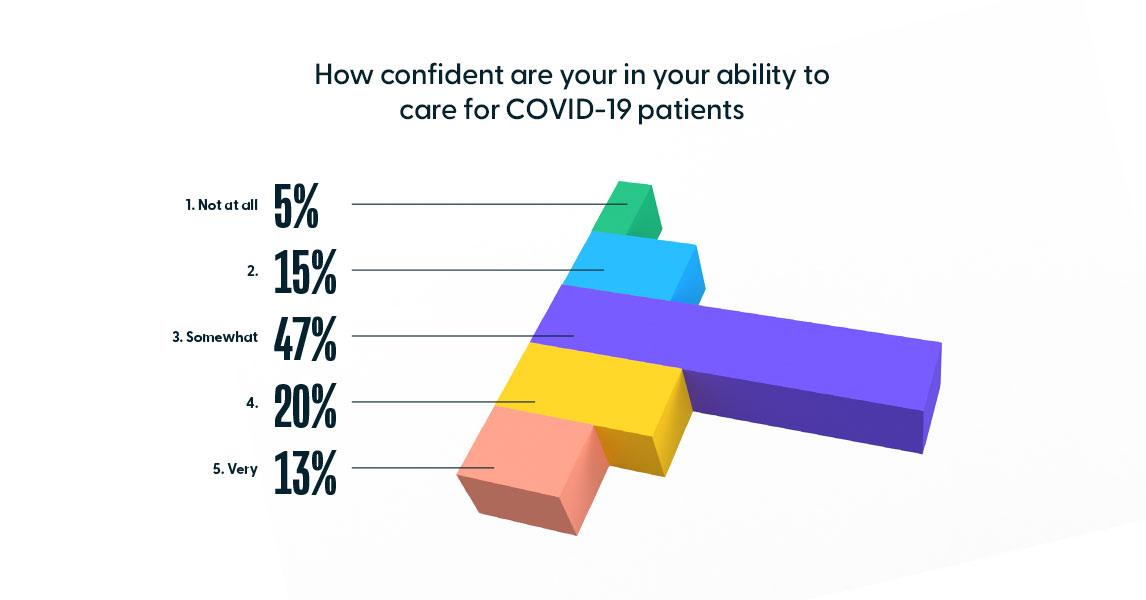
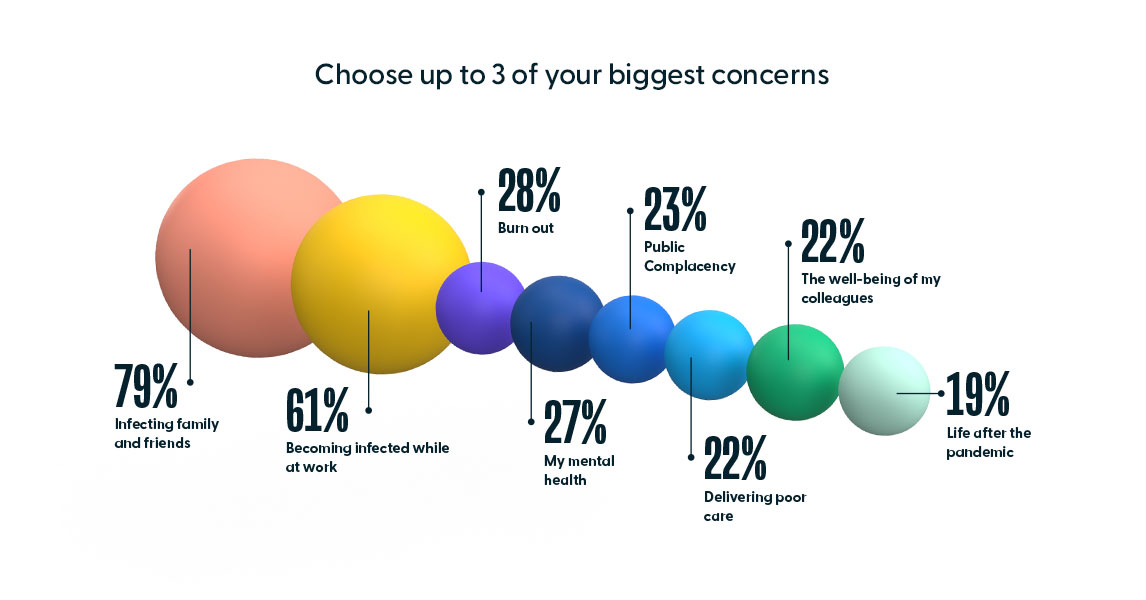
The results reflect the ways in which the pandemic took its toll on healthcare workers. When asked about their top 3 concerns, “infecting their family and friends” was at the top at 79%, followed closely by “becoming infected while at work” at 61%. Amongst the other concerns, 22% of respondents indicated “delivering poor care.” This and the lukewarm confidence levels of the survey indicate concern amongst nurses that could be alleviated with additional training.
Appendix
2021 Nurse Confidence Survey Results
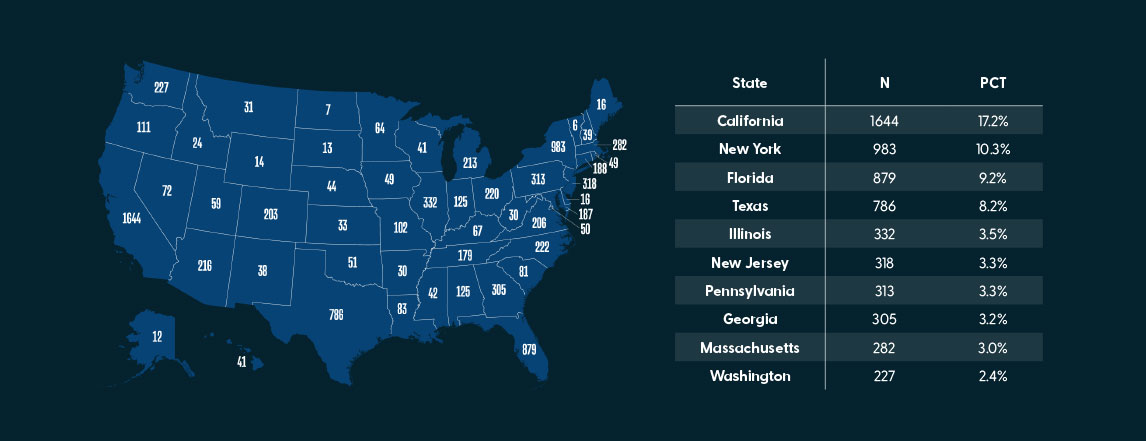
In February 2021, HealthStream conducted an anonymous nurse confidence survey on the Nurse Grid app to better understand how registered nurses rated their own confidence related to resuscitation, and management of specialty-specific clinical problems. In total, 9,556 registered nurses from all 50 states across the U.S. completed the survey, with over half of the participants from the States of California, New York, Florida, Texas, Illinois, New Jersey.
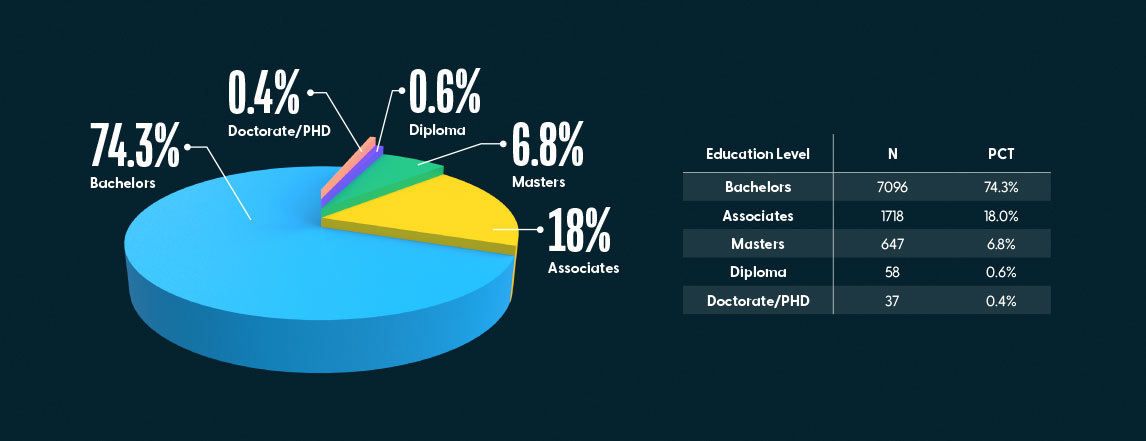
The majority of the participants held a bachelor’s degree (74.3%), followed by a smaller number with an associate degree (18%). 6.8% held a master’s degree, and less than one percent held either a diploma or doctorate degree.
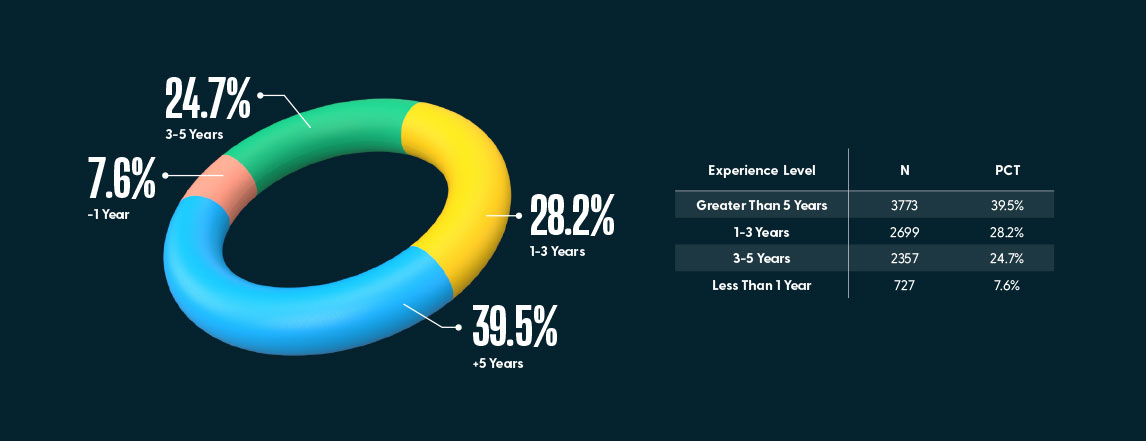
7.6% of the participants were newly graduate nurses with under one year of experience. The remainder (93.4%) of the participants had greater than one year of experience as a registered nurse.
Acute Care, Intensive Care, Emergency, and Labor & Delivery accounted for roughly 80% of the primary specialty areas, with the remaining specialty areas accounting for approximately 5% or less.

